|
|
Post by Nka on Jun 7, 2014 12:36:29 GMT -6
CAN THE HOUSE BE BUILT ENTIRELY WITH MUD?
YES, OF COURSE! ACROSS TIME, DIFFERENT FORMS OF ARCHES, VAULTS AND DOMES HAVE BEEN BUILT. AS FOLLOWS ARE SOME SUCCESSFUL EXAMPLES FROM AROUND THE WORLDS. BUT THE CHALLENGE IS RATHER HOW TO DESIGNED SUCH A MUD TYPE TO APPEAL TO THE LOCAL POPULACE.
Please, add your comments/suggestions/questions to this page and post other examples you come across.
|
|
|
|
Post by Nka on Jun 7, 2014 12:42:45 GMT -6
AN INTRODUCTION TO VAULTED STRUCTURES: Arches, Vaults and Domes (AVD) have been used to build durable structures across time. The advent of reinforced cement concrete, tensile and steel structures brought THE GREAT FORGETTING of the making of vaulted structures with earth under the feet. Read more about AVD: 1-introduction-avd-en.pdf (724.59 KB)
 Nubian Vault Roof Nubian Vault Roof
Economic earth construction designed by Ray Meeker
The structure was built with mud blocks and mortar, stuffed with ceramic products, and fired. The house itself would get fired as a consequence. The fuel required for firing would be largey accountable to the products inside. Mud mortar joints would be made possible as they strengthen after firing. And further economy would result. Ray Meeker's technique offered the possibility of a moderate-cost, yet strong house. Environmentally sound; climatically appropriate. Pucca, yet made of the very basic elements - earth, water and fire.
The simple requirements were accommodated in an equally simple plan - a central dome surrounded by four vaults covering a 700 sq.ft area. There were only two main additions after firing - the entrance canopy as a fifth vault in fired brick and lime mortar, and a partial loft within the highest of the four vaults. Nubian vault construction was followed for all five vaults.
Segmental vault, in “Free spanning” mode, meaning without formwork. This was previously called the Nubian technique, from Egypt, but the Auroville Earth Institute developed it and found new ways to build arches and vaults.
|
|
|
|
Post by Nka on Jun 9, 2014 0:46:08 GMT -6
EXAMPLES OF EARTH BAG DOMES
Karl's Root Cellar


Mindfulness Project site plan -- dome cluster and gazebo, Thailand
|
|
|
|
Post by Nka on Jun 9, 2014 22:43:41 GMT -6
MUSGUM MUD HOUSES
The Musgum is an ethnic group in far north province in Cameroon
Maintenance of a Musgum Dwelling Musgum Mud Houses resembling the shape of beehives or shells.
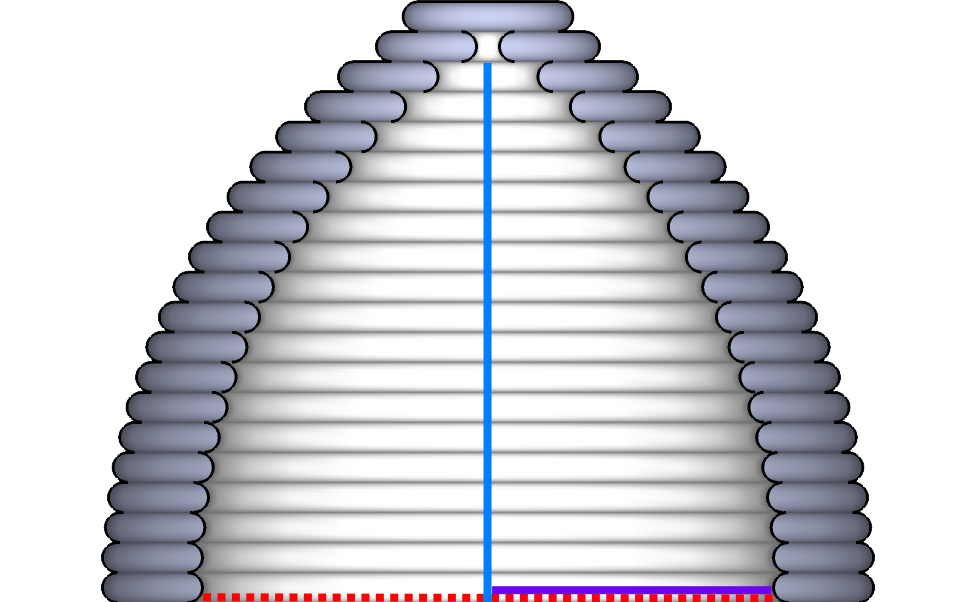
Vaults built in this way can be very slim and use a minimum of material for maximum strength.
The Site Plan of a Compound of mud houses. A characteristic settlement form is the compound, which is a cluster of units linked by walls. The domed huts of the Musgum people are built in shaped mud, a variant of cob. Cob building is the most widely used technique in the world, since no tools are needed- just bare feet, earth and water.
Musgum Mud Houses are Built Using Nature's Arch... The Catenary
The house is created from compressed sun-dried mud. The dwelling has walls that are thicker at the base than at the summit. The reason for this kind of wall is to provide stability to the structure. it is customary to lay the mud spirally in lifts of approximately half a metre, allowing each lift to dry before adding the next.
The name of these houses (‘cases obos’) comes from their similarity with the profile of shells. It is very close to the catenary arch, the ideal mathematical form to bear a maximum weight with minimal material. This profile also reduces the pressure effect of the impact of water drops on the walls. Furthermore, the extraordinary height (up to 9 meters) of these houses provides a comfort climate during hot days. The top of the house is pierced with a circular opening, allowing the air to circulate, resulting in the sensation of freshness. Today, these buildings have become somewhat obsolete, with only a few groups still practicing this ‘cases obos’ type of construction.
Curves and grooves are the language of natural forms. The Musgum house follows the profile of shells – the arc of a chain. Bows and vaults obtained in this way can be very slim and allow the use of a minimum of material for maximum rigidity. The arc adopting the inverted profile will only work in compression and does not produces parasitic twisting or bending moments.
Source: designboom.com
|
|